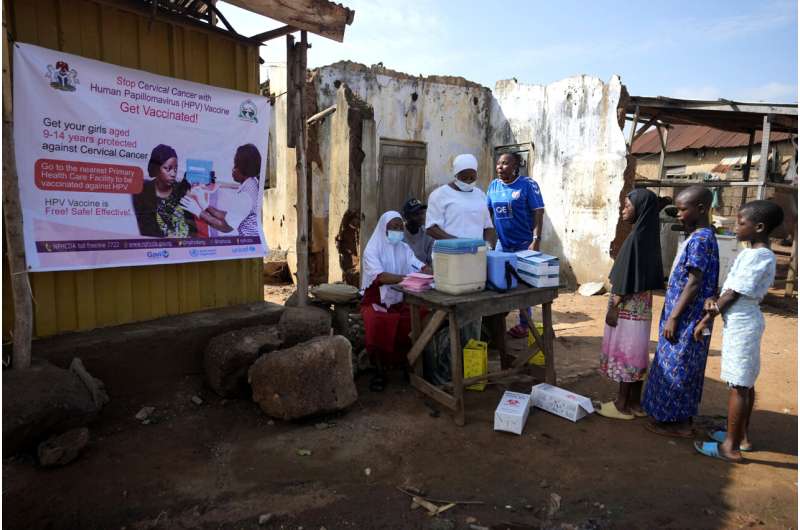
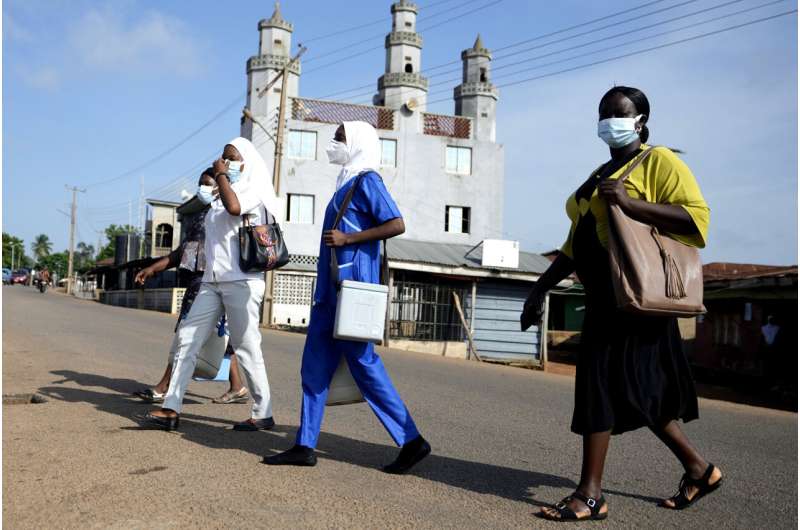
Yunusa Bawa spends a variety of time speaking in regards to the vaccine for the human papillomavirus that’s answerable for practically all instances of cervical most cancers. However on most days, solely two or three individuals permit their daughters to be vaccinated within the rural a part of Nigeria the place he works.
The problem in Sabo neighborhood, on the outskirts of the capital of Abuja, is the unfounded rumor that the HPV vaccine will later preserve younger ladies from giving delivery.
“The rumor is an excessive amount of,” stated Bawa, 42.
As extra African nations attempt to manage extra HPV vaccines, Bawa and different well being employees sort out challenges that sluggish progress, notably misinformation in regards to the vaccine. The World Well being Group’s Africa workplace estimates that about 25% of the inhabitants nonetheless has doubts about it—reflecting issues seen in another elements of the world in early campaigns for the vaccine.
A typical sexually transmitted virus, HPV may cause cervical most cancers, sure different cancers and genital warts. Generally, the virus does not trigger any issues, however some infections persist and ultimately result in most cancers.
Throughout Africa, a mean of 190 ladies died each day from cervical most cancers in 2020, accounting for 23% of the deaths globally and making it the main most cancers killer amongst ladies within the WHO Africa area of 47 nations. Eighteen of the 20 nations with the best charge of cervical most cancers instances on the earth are in Africa. But the area’s HPV vaccination charge has been low.

Greater than half of Africa’s 54 nations—28—have launched the vaccine of their immunization applications, however solely 5 have reached the 90% protection that the continent hopes to realize by 2030. Throughout the area, 33% of younger ladies have been vaccinated with HPV.
It is a stark distinction to most European nations, the place each ladies and boys have been receiving HPV pictures.
A part of why Africa has a excessive burden of cervical most cancers is due to restricted entry to screening for ladies, stated Emily Kobayashi, head of the HPV Program on the vaccines alliance Gavi.
“The elimination technique is an extended sport … however we all know that vaccination is the strongest pillar and one of many best to implement,” Kobayashi stated.
However “it’s one factor to introduce the vaccine, but when the vaccine stays within the fridge, it does not forestall cervical most cancers,” stated Charles Shey Wiysonge, head of the vaccine-preventable ailments program within the WHO’s Africa area. He stated data should be offered by individuals “who’re trusted, people who find themselves near the communities.”
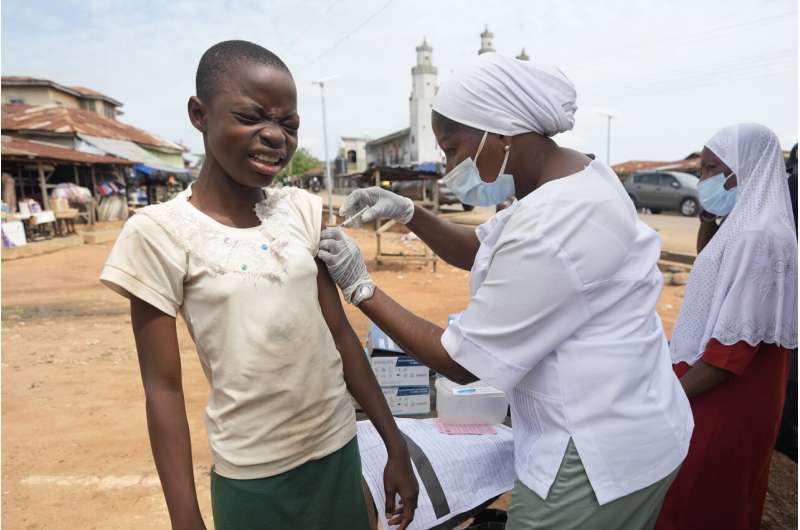
There’s a lengthy historical past of vaccine hesitancy in lots of African nations that’s generally linked to a scarcity of belief in authorities, as one examine revealed within the Nature science journal in Could discovered, giving room for conspiracy theories and misinformation from social media influencers and spiritual leaders.
In Zimbabwe, the place cervical most cancers is essentially the most frequent most cancers amongst ladies, a gaggle of largely ladies generally known as Village Well being Employees have been educated to lift consciousness about cervical most cancers and the HPV vaccine in rural areas. However they battle a excessive stage of hesitancy amongst spiritual sects that discourage followers from fashionable medicines, asking them to rely as an alternative on prayers and “anointed” water and stones.
The ladies who ultimately conform to be screened for cervical most cancers achieve this in secret, stated Zanele Ndlovu, one of many well being employees on the outskirts of Bulawayo metropolis.
For a deeply spiritual nation like Zimbabwe, “the religious leaders have a lot affect that a variety of our time is taken making an attempt to teach individuals in regards to the security of vaccines, or that they don’t seem to be ungodly,” Ndlovu stated.
There are additionally success tales in Africa the place authorities have achieved as much as a 90% vaccination charge. One instance is Ethiopia, which depends closely on spiritual leaders, academics and hotline employees.

In Rwanda, the primary African nation to implement a nationwide HPV vaccination program in 2011, the protection charge has reached 90%. Hesitancy is much less of a problem attributable to vigorous consciousness work that has relied on school-based campaigns and neighborhood outreach applications, stated Dr. Theoneste Maniragaba, director of the most cancers program at Rwanda Biomedical Middle.
Mozambique has deployed school-based applications, a door-to-door strategy and cell outreach for women in hard-to-reach areas that has helped it attain 80% protection charge with the primary of two doses. In Tanzania, the place the HPV vaccine has been in use since at the least 2018, authorities in April launched a marketing campaign to focus on over 5 million ladies and additional increase protection, which has reached 79% of ladies with the primary dose.
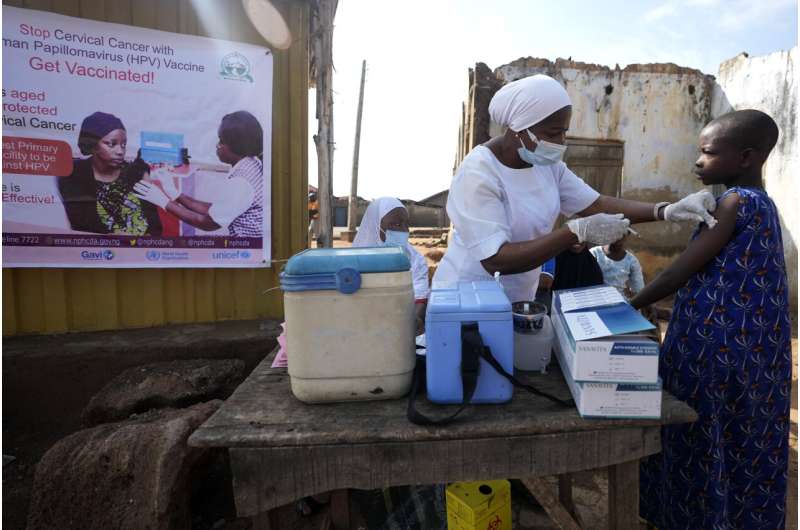
One among Africa’s largest HPV vaccination drives focusing on ladies just lately kicked off in Nigeria, which has procured practically 15 million doses with the assistance of the U.N. kids’s company. It’s going to goal ladies aged 9–14 with single doses that the WHO’s African immunization advisory group has stated is as efficient because the common two doses.
One problem is explaining the HPV vaccination to women forward of the onset of sexual exercise, particularly in conservative societies, stated Dr. Aisha Mustapha, a gynecologist in northern Kaduna state.
Mustapha has been efficiently handled for cervical most cancers. She stated the expertise helps in her conferences with spiritual leaders and in neighborhood outreach applications in Kaduna, the place she leads the Medical Ladies Affiliation of Nigeria.

They attempt to make the women really feel snug and perceive why the vaccine is vital, she stated. That generally requires comedian books and many singing.
“The (cervical) most cancers … is not any respecter of any id,” she stated. “The vaccine is offered, it’s free, it’s secure and efficient.”
© 2024 The Related Press. All rights reserved. This materials will not be revealed, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed with out permission.
Quotation:
Extra African nations deal with HPV vaccination in opposition to cervical most cancers, however hesitancy stays (2024, June 24)
retrieved 24 June 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-06-african-nations-focus-hpv-vaccination.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




















